In the face of rapidly growing global urbanization, the concept of smart cities has emerged as a critical solution for addressing the challenges of modern urban life. With cities around the world becoming more crowded, complex, and interconnected, the need for a technological transformation in urban planning has never been more urgent. Smart cities use cutting-edge technologies to improve the quality of life for their inhabitants, enhance sustainability, and foster greater efficiency across urban systems.
From reducing energy consumption to improving traffic flow and public services, smart cities are poised to fundamentally reshape how we live, work, and interact within our urban environments. In this article, we will explore how smart cities are being developed, the technologies driving their transformation, and the impact they are having on the future of urban life.
Key Takeaway
Smart cities represent the future of urban living, where technology plays a central role in creating more efficient, sustainable, and livable environments. By embracing the tools of the digital age, cities can address the pressing challenges of the 21st century and build a brighter, more connected future for their citizens. As cities continue to evolve, the integration of technology will be essential to shaping urban spaces that meet the needs of diverse populations and foster long-term sustainability.
What is a Smart City?
A smart city is an urban area that uses a variety of digital technologies to enhance performance, well-being, and reduce costs & resource consumption across the city. In a smart city, infrastructure, services, and data networks are all interconnected, enabling intelligent decision-making and improved efficiency. These cities leverage technologies like Internet of Things (IoT) devices, artificial intelligence (AI), big data analytics, cloud computing, and sensor networks to optimize public services and infrastructure.
Rather than relying on traditional urban planning strategies, smart cities integrate innovative tech solutions that monitor and manage everything from traffic to water supply, waste management, healthcare, and energy use. These technological advancements help cities cope with the challenges of climate change, population growth, and resource management, creating a more sustainable and livable environment for residents.
Key Components of Smart Cities
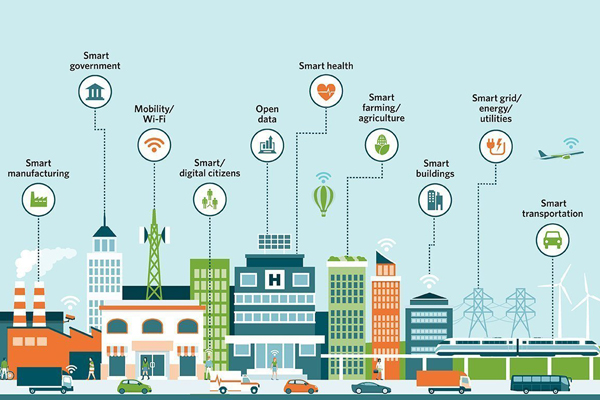
- Internet of Things (IoT):
IoT devices are the backbone of smart cities, connecting physical infrastructure such as roads, buildings, and traffic systems to the digital world. IoT enables real-time monitoring and management of urban elements, providing actionable insights that improve services and quality of life. For example, smart sensors can detect air quality or the availability of parking spaces, while automated systems can regulate traffic lights to ease congestion. - Data Analytics and Big Data:
With vast amounts of data being generated by IoT devices and sensors, smart cities rely heavily on data analytics to turn this information into actionable insights. By analyzing patterns in traffic, energy consumption, or waste production, city officials can make data-driven decisions to optimize urban systems and predict future challenges. The use of big data helps improve everything from public health responses to emergency management. - Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):
AI and ML algorithms can analyze large datasets, recognize patterns, and make real-time predictions that can enhance urban management. For example, AI is increasingly used to predict traffic flow, optimize public transport routes, or even manage energy consumption by automatically adjusting lighting or heating systems. Over time, AI can become more effective as it learns from historical data and evolves to solve increasingly complex urban issues. - Sustainable Infrastructure:
Smart cities focus heavily on sustainability, using technology to reduce environmental impacts. From renewable energy sources to efficient waste management systems, sustainable practices are integrated into every aspect of urban living. Green buildings equipped with smart systems can optimize energy usage, reducing carbon emissions and lowering operating costs. Additionally, smart grids allow cities to better manage electricity distribution, shifting towards renewable energy sources when possible. - Connected Transportation and Mobility:
A significant challenge in modern urban life is traffic congestion and inefficient transportation networks. Smart cities are addressing these issues by creating connected transport systems that integrate various modes of transport, such as electric vehicles, ride-sharing, autonomous vehicles, and public transit. By using real-time data, smart cities can manage traffic flow, reduce congestion, and offer citizens more sustainable transport options. - Smart Healthcare:
The healthcare sector in smart cities uses advanced technology to provide more efficient services, improve patient care, and ensure better outcomes. Digital health records, telemedicine, and wearable health devices all play a role in managing public health. Cities can use data analytics to track disease outbreaks or monitor health trends to make preventative measures more effective. - Smart Governance and Civic Engagement:
Smart cities encourage citizen participation through digital platforms that allow residents to engage with city authorities, report issues, and provide feedback on city services. This helps improve transparency and accountability in governance. Additionally, using open data platforms, governments can share valuable information with citizens and businesses, driving innovation and collaboration within the community.
Technologies Driving Smart Cities
Several key technologies are playing a critical role in the development of smart cities, enabling them to function more efficiently and sustainably.
- IoT Sensors:
IoT sensors are embedded in various elements of a smart city, such as street lights, waste bins, and buildings, to collect real-time data on usage, energy consumption, and environmental conditions. For instance, smart streetlights equipped with IoT sensors can adjust their brightness based on the time of day, reducing energy consumption and lowering costs. - Big Data Platforms:
To handle the large amounts of data generated by smart city infrastructure, big data platforms are used to store, process, and analyze the data in real-time. These platforms provide a central repository of information that city officials can access to make informed decisions. - Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing allows cities to store vast amounts of data and applications in remote servers, providing scalability, flexibility, and accessibility. This allows smart city solutions to be integrated and managed efficiently without requiring significant local infrastructure. - Blockchain:
Blockchain technology has the potential to transform various aspects of smart city management, from secure data sharing to improving transparency in government processes. Blockchain can be used to streamline transactions, secure identities, and enable decentralized applications that enhance urban services.
Benefits of Smart Cities
- Enhanced Sustainability:
Through the use of green technologies and energy-efficient systems, smart cities help reduce carbon emissions, conserve resources, and minimize waste. Cities can use smart grids to better manage energy distribution, and renewable energy sources like solar or wind power can be integrated into the urban infrastructure. - Improved Quality of Life:
The increased use of technology and data analytics helps improve the day-to-day lives of citizens. For example, traffic congestion can be reduced through smart traffic management, while smart healthcare systems provide residents with better access to medical services. - Increased Efficiency:
Smart city technologies optimize urban infrastructure, reducing inefficiencies and lowering costs. Automated systems, like those used for waste management or energy distribution, ensure that resources are used more effectively, saving money and improving service delivery. - Economic Growth and Innovation:
By creating an environment conducive to technological innovation, smart cities can attract new businesses, talent, and investments. Furthermore, the open data platforms in these cities foster innovation, with startups and entrepreneurs developing new solutions to solve urban challenges.
Challenges in Developing Smart Cities

Despite the significant advantages, the development of smart cities also presents several challenges:
- Privacy Concerns:
With the vast amounts of data being collected in smart cities, privacy concerns are a significant issue. Ensuring that data is handled securely and transparently is crucial to gaining public trust. - High Costs:
Building the infrastructure for a smart city requires substantial investment in both technology and physical infrastructure. The costs involved may be a barrier for many cities, particularly those in developing countries. - Digital Divide:
Access to technology is not equal for all residents. Some communities may lack the digital literacy or resources necessary to benefit fully from smart city innovations. Bridging this gap is critical to ensuring that all citizens have equal access to the advantages of smart cities. - Interoperability:
As smart cities involve a wide range of different technologies and systems, ensuring that these systems can work together seamlessly is essential for effective urban management. Interoperability issues can lead to inefficiencies and complications in the functioning of smart city systems.
Also Read : Unlocking The Power Of Big Data: Transforming Insights In To Action
Conclusion
Smart cities are not just a futuristic concept but a rapidly developing reality that is transforming urban living around the world. By harnessing the power of data, technology, and innovation, these cities are setting the stage for a new era of urban life that is more sustainable, efficient, and connected than ever before. While there are challenges to overcome, the potential benefits of smart cities—improved quality of life, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced economic growth—are undeniable.
(FAQs)
What is the main goal of a smart city?
The primary goal of a smart city is to use technology to enhance urban living by improving efficiency, sustainability, and quality of life through the integration of connected systems and data-driven decision-making.
What technologies are used in smart cities?
Smart cities use a variety of technologies, including the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), big data analytics, cloud computing, and smart sensors to manage and optimize urban systems.
How do smart cities reduce environmental impact?
Smart cities use green technologies such as energy-efficient buildings, smart grids, and renewable energy sources to reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and decrease carbon emissions.
Can smart cities improve public transportation?
Yes, smart cities integrate connected transportation systems to improve the efficiency and sustainability of public transport. Real-time data helps optimize routes, reduce congestion, and enhance mobility options for residents.
Are smart cities safe?
While smart cities provide significant benefits, they also introduce new cybersecurity risks. Protecting data and infrastructure from cyberattacks is a key consideration in smart city development.
How do smart cities impact local businesses?
Smart cities foster innovation by providing a more connected environment and open data platforms, helping local businesses grow. By streamlining services and improving infrastructure, smart cities also create a more conducive environment for entrepreneurship.
Are smart cities only for developed countries?
No, while many smart city projects are located in developed countries, developing nations are also exploring the potential of smart cities to solve urbanization challenges and improve infrastructure.

